The REPL
If you’ve followed the instructions in Installation, your Emacs is now ready to start playing. Otherwise, i’ll wait for you: when you’re ready, just come back here and proceed to the following sections.
Starting the REPL
To start a Scheme REPL (meaning, a Scheme process offering you a
Read-Eval-Print Loop), Geiser provides the generic interactive command
geiser. If you invoke it (via, as is customary in Emacs,
M-x geiser), you’ll be saluted by a prompt asking which one of
the supported implementations you want to launch—yes, you can stop the
asking, see
below.
Tabbing for completion will offer you, as of this writing, guile,
racket, chicken, mit, chibi and chez.
Just choose your poison, and a new REPL buffer will pop up (by default,
the REPL will appear in a new window: if that annoys you, just set
geiser-repl-use-other-window to nil and the current window
will be used).
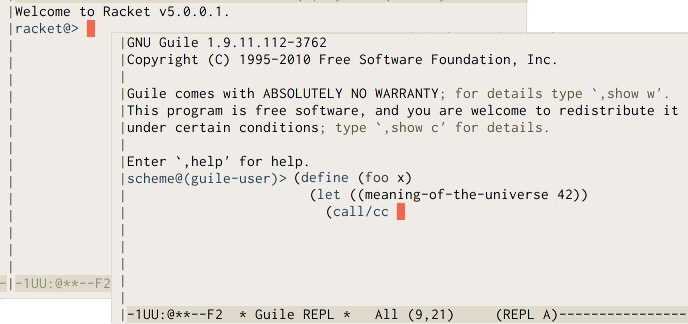
If all went according to plan, you’ll be facing an
implementation-dependent banner, followed by an interactive prompt.
Going according to plan includes having the executable of the Scheme you
chose in your path. If that’s not the case, you can tell Emacs where it
is, as described in
a moment.
Returning to our REPL, the first thing to notice is that the funny
prompt is telling you your current module: its name is the part just
after the @ sign (in Guile, that means guile-user, while
Racket’s and Chicken’s top namespaces don’t have a name;
cf. discussion in
Switching context).
Other than that, this is pretty much equivalent to having a
command-line interpreter in a terminal, with a bunch of add-ons that
we’ll be reviewing below. You can start typing sexps right there:
Geiser will only dispatch them for evaluation when they’re complete,
and will indent new lines properly until then. It will also keep
track of your input, maintaining a history file that will be reloaded
whenever you restart the REPL.
If you’re not happy with the faces Geiser is using for the REPL’s prompt
and evaluated input, you can customise
geiser-font-lock-repl-prompt and
geiser-font-lock-repl-input to better-looking faces.
Connecting to an external Scheme
There’s an alternative way of starting a Geiser REPL: you can connect to an external Scheme process, provided it’s running a REPL server at some known port. How to make that happen depends on the Scheme implementation.
If you use Guile, you just need to start your Guile process (possibly
outside Emacs) passing to it the flag --listen. This flag accepts
an optional port as argument (as in --listen=1969), if you don’t
want to use the default.
In Racket, you have to use the REPL server that comes with Geiser. To
that end, put Geiser’s Racket scheme directory in Racket’s
collection search path and invoke start-geiser (a procedure in
the module geiser/server) somewhere in your program, passing it
the desired port and, if desired, network interface name. This
procedure will start the REPL server in a separate thread. For an
example of how to do that, see the script bin/geiser-racket.sh in
the source distribution, or, if you’ve compiled Geiser,
bin/geiser-racket-noinst in the build directory, or, if you’ve
installed Geiser, geiser-racket in
<installation-prefix>/bin. These scripts start a new interactive
Racket that is also running a REPL server (they also load the errortrace
library to provide better diagnostics, but that’s not strictly needed).
With your external Scheme process running and serving, come back to Emacs and execute M-x geiser-connect, M-x connect-to-guile or M-x connect-to-racket. You’ll be asked for a host and a port, and, voila, you’ll have a Geiser REPL that is served by the remote Scheme process in a dedicated thread, meaning that your external program can go on doing whatever it was doing while you tinker with it from Emacs. Note, however, that all Scheme threads share the heap, so that you’ll be able to interact with those other threads in the running Scheme from Emacs in a variety of ways. For starters, all your (re)definitions will be visible everywhere. That’s dangerous, but will come in handy when you need to debug your running web server.
The connection between Emacs and the Scheme process goes over TCP, so it can be as remote as you need, perhaps with the intervention of an SSH tunnel.
First aids
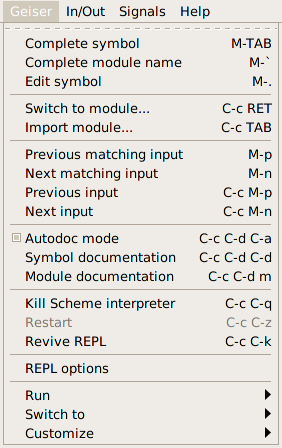
A quick way of seeing what else Geiser’s REPL can do for you, is to display the corresponding entry up there in your menu bar. No, i don’t normally use menus either; but they can come in handy until you’ve memorized Geiser’s commands, as a learning device. And yes, i usually run Emacs inside a terminal, but one can always use La Carte to access the menus in a convenient enough fashion.
Or just press C-h m and be done with that.
Among the commands at your disposal, we find the familiar input navigation keys, with a couple twists. By default, M-p and M-n are bound to matching items in your input history. That is, they’ll find the previous or next sexp that starts with the current input prefix (defined as the text between the end of the prompt and your current position, a.k.a. point, in the buffer). For going up and down the list unconditionally, just use C-c M-p and C-c M-n. In addition, navigation is sexp-based rather than line-based.
There are also a few commands to twiddle with the Scheme process. C-c C-q will gently ask it to quit, while C-u C-c C-q will mercilessly kill the process (but not before stowing your history in the file system). Unless you’re using a remote REPL, that is, in which case both commands will just sever the connection and leave the remote process alone. If worse comes to worst and the process is dead, C-c C-z will restart it. However, the same shortcut, issued when the REPL is alive, will bring you back to the buffer you came from, as explained in this section.
The remaining commands are meatier, and deserve sections of their own.
Switching context
In tune with Geiser’s
modus operandi,
evaluations in the REPL take place in the namespace of the current
module. As noted above, the REPL’s prompt tells you the name of the
current module. To switch to a different one, you can use the command
geiser-repl-switch-to-module, bound to C-c C-m. You’ll
notice that Geiser simply uses a couple of meta-commands provided by
the Scheme REPL (the stock ,m in Guile and Chicken and the
(geiser-defined) ,enter in Racket), and that it doesn’t even
try to hide that fact. That means that you can freely use said native
ways directly at the REPL, and Geiser will be happy to oblige. In
Racket, ,enter works like Racket’s standard enter!
form, but you can also provide a path string as its argument (e.g.,
,enter "/tmp/foo.rkt" is equivalent to ,enter (file
"/tmp/foo.rkt")). Like enter!, ,enter accepts also
module names (as in, say, ,enter geiser/main). As
mentioned, in Guile and Chicken, ,m is used as is.
Once you enter a new module, only those bindings visible in its
namespace will be available to your evaluations. All Schemes supported
by Geiser provide a way to import new modules in the current namespace.
Again, there’s a Geiser command, geiser-repl-import-module, to
invoke such functionality, bound this time to C-c C-i. And, again,
you’ll see Geiser just introducing the native incantation for you, and
you’re free to use such incantations by hand whenever you want.
One convenience provided by these two Geiser commands is that completion is available when introducing the new module name, using the TAB key. Pressing it at the command’s prompt will offer you a prefix-aware list of available module names.
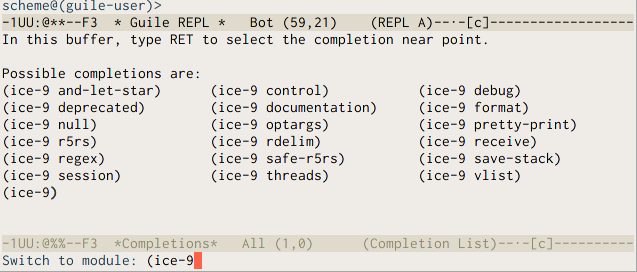
Which brings me to the next group of REPL commands.
Completion and error handling
We’ve already seen Geiser completion of module names in action at the minibuffer. You won’t be surprised to know that it’s also available at the REPL buffer itself. There, you can use either C-. or M-` to complete module names, and TAB or M-TAB to complete identifiers. Geiser will know what identifiers are bound in the current module and show you a list of those starting with the prefix at point. Needless to say, this is not a static list, and it will grow as you define or import new bindings in the namespace at hand. If no completion is found, TAB will try to complete the prefix after point as a module name.
REPL buffers use Emacs’ compilation mode to highlight errors reported by
the Scheme interpreter, and you can use the next-error command
(M-g n) to jump to their location. By default, every time you
enter a new expression for evaluation old error messages are forgotten,
so that M-g n will always jump to errors related to the last
evaluation request, if any. If you prefer a not-so-forgetful REPL, set
the customization variable geiser-repl-forget-old-errors-p to
nil. Note, however, that even when that variable is left as
t, you can always jump to an old error by moving to its line at
the REPL and pressing RET. When your cursor is away from
the last prompt, TAB will move to the next error in the
buffer, and you can use BACKTAB everywhere to go to the
previous one.
Caveat about completion & the REPL
It is possible for Geiser to hang your Emacs process when trying to complete symbols. This can happen in the REPL itself or even in a Scheme buffer that is attached to the REPL process. If this happens, you’ve probably entered a module that changes the REPL prompt from what Geiser was expecting to see.
Unfortunately, there’s no general solution for this issue right now (as it is a daunting task to try to make a regexp that can encompass all possible REPL prompts). The best solution for now is to fix this issue on a case-by-case basis by adjusting your prompt regexp variable so that it matches the default prompt as well as your Scheme module’s special prompt.
For example, XREPL is a Racket module that implements a better Racket REPL. You might be interested in toying around with some of its functions, but when you try to enter XREPL via, say, C-c C-m xrepl, you’ll notice that the REPL prompt has changed to something like this:
<pkgs>/xrepl-lib/xrepl/main>
If you start typing symbols, and then you try to auto-complete those symbols, your Emacs process may hang. This is because Geiser expects the REPL prompt to match this regexp (for Racket):
"\\(mzscheme\\|racket\\)@[^ ]*> "
Therefore, we can fix this issue by changing our default prompt regexp like so:
(setq geiser-racket--prompt-regexp "<pkgs>.*> \\|\\(mzscheme\\|racket\\)@[^ ]*> ")
Note that you may have to run M-x geiser-reload after setting this variable so that your changes will take effect.
Again, you’ll have to change the regexp to fit every prompt that causes this issue, but the only alternative (that we can think of right now) is to create a regexp that will match every possible prompt. Obviously, that is going to be more than a little tricky. However, if you have a better solution than that, please share it with the Geiser developers; we’ll be more than happy to hear it.
Autodoc and friends
Oftentimes, there’s more you’ll want to know about an identifier besides its name: What module does it belong to? Is it a procedure and, if so, what arguments does it take? Geiser tries to help you answering those questions too.
Actually, if you’ve been playing with the REPL as you read, you might have notice some frantic activity taking place in the echo area every now and then. That was Geiser trying to be helpful (while, hopefully, not being clippy), or, more concretely, what i call, for want of a better name, its autodoc mode. Whenever it’s active (did you notice that A in the mode-line?), Geiser’s gerbils will be scanning what you type and showing (unless you silence them with C-c C-d C-a) information about the identifier nearest to point.
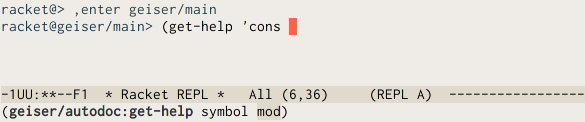
If that identifier corresponds to a variable visible in the current namespace, you’ll see the module it belongs to and its value. For procedures and macros, autodoc will display, instead of their value, the argument names (or an underscore if Geiser cannot determine the name used in the definition). Optional arguments are surrounded by parentheses. When the optional argument has a default value, it’s represented by a list made up of its name and that value. When the argument is a keyword argument, its name has “#:” as a prefix.
If that’s not enough documentation for you, C-c C-d d will open
a separate documentation buffer with help on the symbol at point.
This buffer will contain implementation-specific information about the
identifier (e.g., its docstring for Guile, or its contract, if any,
for Racket), and a handy button to open the corresponding manual entry
for the symbol, which will open an HTML page (for Racket and Chicken)
or the texinfo manual (for Guile). If you’d rather go directly to the
manual, try C-c C-d i, which invokes
geiser-doc-look-up-manual as the handy button does.
Geiser can also produce for you a list, classified by kind, of the identifiers exported by a given module: all you need to do is press C-c C-d m, and type or complete the desired module’s name.
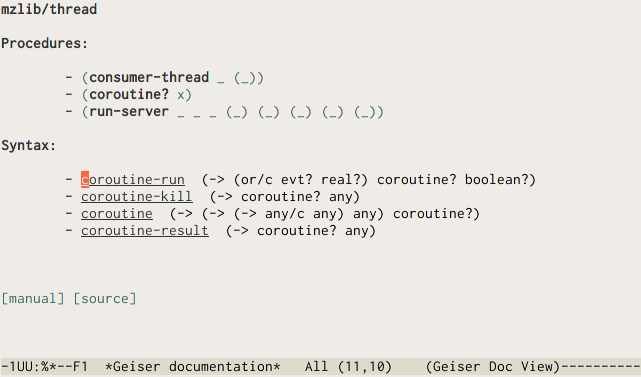
The list of exported bindings is shown, again, in a buffer belonging to Geiser’s documentation browser, where you have at your disposal a bunch of navigation commands listed in our cheat-sheet.
We’ll have a bit more to say about the documentation browser in a later section.
If that’s still not enough, Geiser can jump, via M-., to the symbol’s definition. A buffer with the corresponding file will pop up, with its point resting upon the identifier’s defining form. When you’re done inspecting, M-, will bring you back to where you were. As we will see, these commands are also available in Scheme buffers. M-. also works for modules: if your point is on an unambiguous module name, the file where it’s defined will be opened for you.
Seeing is believing
In schemes that support images as values (currently, that means Racket), the REPL will display them inline if you’re using them in a graphics-aware Emacs.
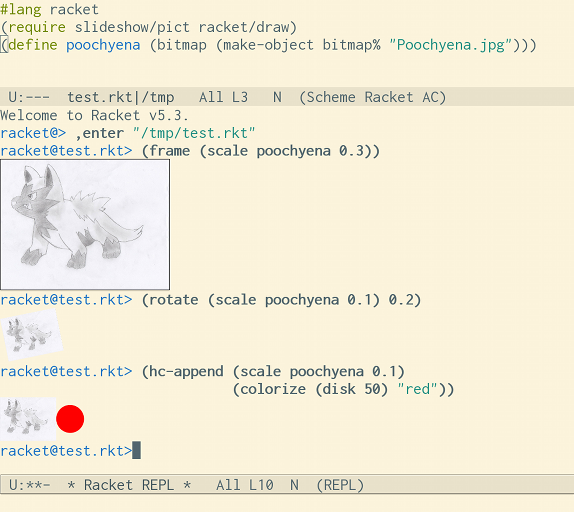
For the terminal, images will appear as buttons: press return on them to
invoke an external viewer (configurable via geiser-image-viewer)
that will show you the image at hand. You can also ask for the same
behaviour on all emacsen by customising
geiser-repl-inline-images-p to nil.
Geiser keeps a cache of the last displayed images in the directory
geiser-image-cache-dir, which defaults to the system’s temp
directory, with up to geiser-image-cache-keep-last files. You
can invoke the external image viewer on any of them with M-x
geiser-view-last-image, which takes a prefix argument to indicate which
image number you want, 0 corresponding to the newest one.
Customization and tips
The looks and ways of the REPL can be fine-tuned via a bunch of customization variables. You can see and modify them all in the corresponding customization group (by using the menu entry or the good old M-x customize-group geiser-repl), or by setting them in your Emacs initialisation files (as a rule, all knobs in Geiser are tunable this way: you don’t need to use customization buffers if you don’t like them).
I’m documenting below a proper subset of those settings, together with some related tips.
Choosing a Scheme implementation
Instead of using the generic geiser command, you can directly
start your Scheme of choice using any of the following commands:
run-racketrun-guilerun-chickenrun-mitrun-chibirun-chez
In addition, the
variable geiser-active-implementations contains a list of those
Schemes Geiser should be aware of. Thus, if you happen to be, say, a
racketeer not to be beguiled by other schemes, you can tell Geiser to
forget about the richness of the Scheme ecosystem with something like:
(setq geiser-active-implementations '(racket))
in your initialisation files.
When starting a new REPL, Geiser assumes, by default, that the corresponding Scheme binary is in your path. If that’s not the case, the variables to tweak are (depending on which Scheme you choose):
geiser-guile-binarygeiser-racket-binarygeiser-chicken-binarygeiser-mit-binarygeiser-chibi-binarygeiser-chez-binary
They should be set to a string with the full path to the requisite binary.
Before starting the REPL, Geiser will check whether the version of your
Scheme interpreter is good enough. This means that it will spend a
couple tenths of a second launching and quickly discarding a Scheme
process, but also that the error message you’ll get if you’re on the
wrong Scheme version will be much more informative. If you one to
avoid version checks, just check
geiser-repl-skip-version-check-p to t in your
configuration.
Init files and load paths
The startup behaviour of the REPL can be also fine tuned with a couple more initialisation parameters.
Many Scheme implementations provide a configuration variable to specify
a Geiser-specific init file (e.g., geiser-guile-init-file for
Guile), and, sometimes a global list of paths to add to the
interpreter’s load path (that’d be geiser-guile-load-path for
Guile).
There is also a generic mechanism to specify how to add directories to
the initial load path when geiser-repl-current-project-function
is set: you can then customize geiser-repl-add-project-paths to a
list of subdirectories of the project’s root to add to the load path.
When this option is set, the working directory of the REPL’s buffer
(i.e., the value of the elisp variable default-directory) will be
set to the directory returned by
geiser-repl-current-project-function).
These variables controlling your scheme’s initialisation process are good candidates for an entry in a project’s .dir-locals.el file, so that they are automatically set to a sensible value whenever you start a REPL in the project’s directory.
Startup waiting time
When starting a scheme implementation in old or very busy computers,
Geiser might have to wait a bit more than it expects (which is ten
seconds, or ten thousand milliseconds, by default). If you find that
Geiser is giving up too quickly and complaining that no prompt was
found, try to increase the value of geiser-repl-startup-time to,
say, twenty seconds:
(setq geiser-repl-startup-time 20000)
If you prefer, you can use the customize interface to, well, customise the above variable’s value.
History
By default, Geiser won’t record duplicates in your input history. If you
prefer it did, just set geiser-repl-history-no-dups-p to
nil. History entries are persistent across REPL sessions:
they’re saved in implementation-specific files whose location is
controlled by the variable geiser-repl-history-filename. For
example, my Geiser configuration includes the following line:
(setq geiser-repl-history-filename "~/.emacs.d/geiser-history")
which makes the files geiser-history.guile and geiser-history.racket to live inside my home’s .emacs.d directory.
Autodoc
If you happen to love peace and quiet and prefer to keep your REPL’s
echo area free from autodoc’s noise, geiser-repl-autodoc-p is the
customization variable for you: set it to nil and autodoc will be
disabled by default in new REPLs. You can always bring the fairies
back, on a per-REPL basis, using C-c C-d C-a.
Remote connections
When using any of the connection commands (e.g. geiser-connect,
connect-to-guile, connect-to-racket, etc.) you’ll be
prompted for a host and a port, defaulting to “localhost” and 37146.
You can change those defaults customizing
geiser-repl-default-host and geiser-repl-default-port,
respectively.
Killing REPLs
If you don’t want Emacs to ask for confirmation when you’re about to
kill a live REPL buffer (as will happen, for instance, if you’re exiting
Emacs before closing all your REPLs), you can set the flag
geiser-repl-query-on-kill-p to nil. On a related note,
the customizable variable geiser-repl-query-on-exit-p controls
whether Geiser should ask for confirmation when you exit the REPL
explicitly (via, say, C-c C-q, as opposed to killing the buffer),
and is set to nil by default.